- D-47, Mahavir Nagar Society, Borivali (West), Mumbai - 400092
- Get Direction
- +91 8850448675
- nova.eye.dental@gmail.com
- D-47, Mahavir Nagar Society, Borivali (West), Mumbai - 400092
- Get Direction
- +91 8850448675
- nova.eye.dental@gmail.com
Treatments
Medical Retinal (Diabetic retinopathy & screening)
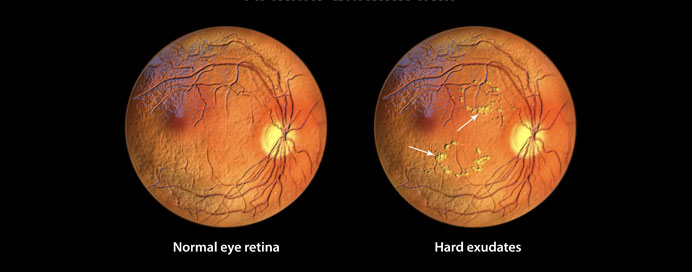
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that affects the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. High blood sugar levels can damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, leading to leakage, bleeding, or abnormal vessel growth, which can cause vision loss if untreated. Medical retina care involves early detection through regular eye screenings, often using retinal photography or optical coherence tomography (OCT). Treatment options include laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, and strict blood sugar control. Early diagnosis and timely intervention are crucial to preserving vision and preventing blindness in diabetic patients.
- Caused by damage to retinal blood vessels due to diabetes
- Early stages may have no symptoms – regular screening is essential
- Screening methods: retinal photography, OCT, and dilated eye exams
- Two main types: non-proliferative and proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- Risk factors: long-standing diabetes, poor sugar control, hypertension
- Good control of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol reduces risk