- D-47, Mahavir Nagar Society, Borivali (West), Mumbai - 400092
- Get Direction
- +91 8850448675
- nova.eye.dental@gmail.com
- D-47, Mahavir Nagar Society, Borivali (West), Mumbai - 400092
- Get Direction
- +91 8850448675
- nova.eye.dental@gmail.com
Treatments
Glaucoma
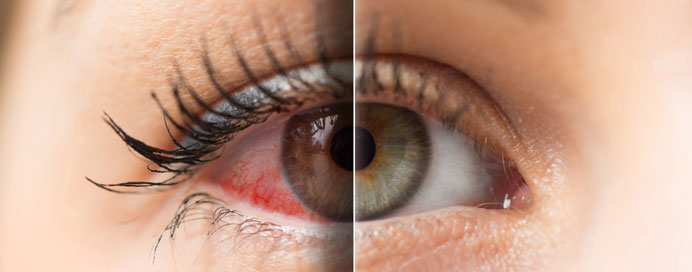
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, usually due to increased intraocular pressure (IOP). This damage can lead to gradual vision loss and, if untreated, permanent blindness. Often called the “silent thief of sight,” glaucoma may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages, making regular eye check-ups essential for early detection. There are different types of glaucoma, including open-angle glaucoma (most common) and angle-closure glaucoma. Treatment focuses on lowering eye pressure through medications, laser therapy, or surgery to prevent further damage to the optic nerve.
- Definition: Eye disease that damages the optic nerve, often due to high eye pressure.
- Nicknamed: “Silent thief of sight” because early stages are symptomless.
- Types: Open-angle glaucoma, angle-closure glaucoma, congenital glaucoma, secondary glaucoma.
- Symptoms (late stage): Gradual loss of peripheral vision, blurred vision, halos around lights, eye pain (in some types).
- Risk factors: Age over 40, family history, diabetes, high eye pressure, long-term steroid use.
- Diagnosis: Tonometry (eye pressure check), optic nerve examination, visual field testing.
- Treatment: Eye drops, oral medications, laser treatment, surgery.